


When you work out the slope of the straight line joining (a,f(a)) to (b,f(b)), it comes out to be
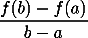
It's no surpise that this is the quantity from the statement of the theorem, because that's really exactly what the mean value theorem says:
Provided f is suitably continuous and differentiable, there is a point in (a,b) at which the instantaneous slope of f is the same as the slope of the straight line joining the values of f at a and b.
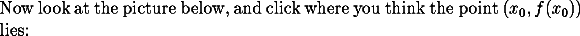

Analysis WebNotes by John Lindsay Orr.
Comments to the author: jorr@math.unl.edu
All contents copyright (C) 1996 John L. Orr University of Nebraska--Lincoln All rights reserved
Last modified: May 1996